Data and Information for SS1
Definition of Data
Data are raw facts. They are figures, words and symbols that have not been processed or put into meaningful form. Data can be referred to as raw material from which information is produced.
Types of data
1. Numeric data: Data consisting of digits and not letters of alphabets or special character. E.g. 0 – 9
2. Alphabetic data: Data consisting of letters and not digits or special characters. A-Z and a-z
3. Alpha-numeric data: Data consisting of digits, alphabets as well special characters. Ussm12, #, !, ?, etc.
Sources of data
Data could be gathered or collected from various sources. Some of the sources include the following:
i. Federal Office of Statistics
ii. National Population Commission
iii. Independent Electoral Commission
iv. Examination Bodies
v. School attendance Register
vi. Bank Statement
Definition of Information
Information is processed data.
Sources of information
Information could be gathered from different sources. Some of the sources of information include the following:
i. Radio
ii. Television
iii. Newspaper
iv. Computer
Qualities of good information
1. Relevance: It must be suitable for the purpose it is required for.
2. Accurate: It be free from errors
3. Availability: It should be easy to obtain or access
4. Timely: It should be available at the right time
5. Comprehensive/Completeness: It should contain all necessary details
6. Reliability: It should come from a reliable source.
Processing of Data into Information
The processing of data into information consist a combination of activities and procedures. Some of the ways in which raw data can be converted into information are:
Collecting : Data to be processed need to be gathered from various sources
Classifying: This is the process of identifying certain characteristics in an items of data and putting them into categories or groups according to those characteristics
Sorting : Sorting takes the form of arranging data into a predefined order of sequence.
Editing: This takes the form of correcting mistakes from the body of data.
Calculating : This is by performing arithmetic manipulation such as adding, subtracting, dividing and multiplication
Translating : This is the process of changing the language form of a data into another.
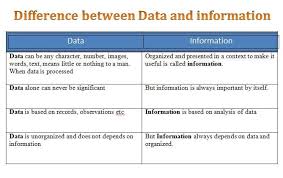
Difference between Data and Information
Data Information
1. Raw facts 1. Processed data
2. Unorganized array of elements 2. Arranged element
3. Unanalyzed sets of element 3. Analyzed element
4. It makes no meaning 4. It is meaningful